Understanding CFD Trading
What is CFD Trading?
CFD stands for Contract for Difference. At its core, CFD trading enables investors to speculate on the price movements of various financial instruments, including stocks, indices, commodities, and currencies, without owning the underlying asset. Instead, traders enter into a contract with a broker, agreeing to exchange the difference in the asset’s value from the time the contract is opened to when it is closed.
How Does CFD Trading Work?
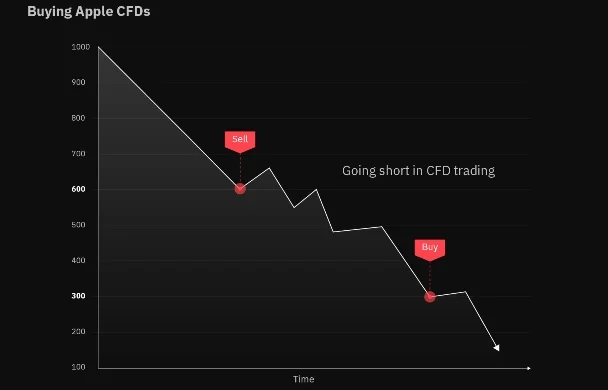
One of the key features of CFD trading is leverage, which allows traders to control a larger position size with a relatively small amount of capital. This amplifies both potential profits and losses, making CFD trading a high-risk, high-reward endeavor. Additionally, traders have the flexibility to go long (buy) or short (sell) on CFD contracts, enabling them to profit from both rising and falling markets.
Advantages of CFD Trading
Access to Global Markets: CFD trading provides access to a wide range of global markets, allowing traders to diversify their portfolios and capitalize on opportunities across various asset classes.
Leverage: The ability to trade on margin means that traders can potentially generate higher returns from their investments. However, it’s important to exercise caution, as leverage can also magnify losses.
Flexibility: With CFD trading, there are no ownership rights to the underlying asset, providing flexibility in terms of entry and exit points, as well as the ability to implement a variety of trading strategies.
Risks of CFD Trading
Market Volatility: Financial markets are inherently volatile, and CFD trading amplifies this volatility due to leverage. Sudden price fluctuations can result in significant gains or losses, depending on the direction of the trade.
Leverage and Margin Calls: While leverage can amplify profits, it also exposes traders to the risk of margin calls, where they may be required to deposit additional funds to maintain their positions or risk having them forcibly closed by the broker.
Counterparty Risk: CFD trading involves entering into contracts with brokers, which exposes traders to counterparty risk. It’s essential to choose reputable brokers with robust risk management practices.
Getting Started with CFD Trading
Choose a Reliable Broker: Selecting a reputable broker is paramount to success in CFD trading. Look for brokers that are regulated by recognized authorities and offer competitive trading conditions, including tight spreads, reliable execution, and comprehensive customer support.
Educate Yourself: Before diving into CFD trading, take the time to educate yourself about the intricacies of the market, including risk management strategies, technical and fundamental analysis techniques, and trading psychology.
Start Small: Begin with a demo account or trade with small amounts of capital to gain experience and confidence in your trading abilities before committing larger sums of money.
Conclusion
CFD trading offers a plethora of opportunities for traders to profit from the dynamic movements of financial markets. However, it’s essential to approach it with caution and diligence, as the potential for both rewards and risks is substantial. By understanding the fundamentals, implementing sound risk management practices, and continually educating yourself, you can navigate the world of CFD trading with confidence and success.